Amazon Web Services (AWS) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a cloud computing service that allows users to create and manage their own virtual network in the cloud. This allows users to have complete control over their network and resources, including the ability to customize subnetting for their VPC.
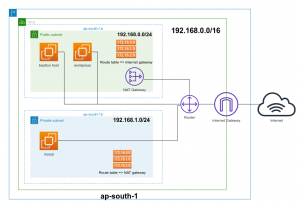
Subnets in AWS VPC are used to divide a VPC into multiple logical networks. This allows users to isolate resources and control access to those resources. Subnets can be either public or private, with public subnets having access to the internet and private subnets not having access to the internet.
Creating subnets in AWS VPC is easy and can be done through the AWS Management Console. First, the user must select their VPC and then click on the “Subnets” tab. From there, the user can select “Create Subnet” and enter the name, VPC, and availability zone for the subnet. They can also specify whether the subnet is public or private.
Once the subnet is created, the user can then add resources to the subnet, such as EC2 instances or RDS databases. The user can also control access to the subnet through the use of security groups and network ACLs.
One important consideration when creating subnets in AWS VPC is the CIDR block. CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) blocks are used to specify the range of IP addresses that can be used in a subnet. The user must specify a CIDR block when creating a subnet, and the CIDR block must be within the VPC’s CIDR block range.
Another important consideration is the availability zone for the subnet. AWS VPC allows users to create subnets in multiple availability zones within a region. This provides high availability and redundancy for the subnet and its resources.
Subnetting can also be useful for segmenting a VPC into different environments, such as development, staging, and production. This allows users to isolate resources and control access between environments.
There are also additional benefits to using subnets in AWS VPC. For example, users can create a NAT gateway in a public subnet and use it to enable internet access for private subnets. This allows resources in the private subnet to access the internet without having a public IP address.
Users can also use VPC peering to connect two VPCs together and share resources between them. This can be useful for creating a more complex network architecture, such as connecting a VPC in one region to a VPC in another region.
Conclusion
Subnets in AWS VPC provide users with the ability to customize and control their virtual network in the cloud. Subnetting allows users to segment their VPC into multiple logical networks, isolate resources, and control access to those resources. It also provides benefits such as high availability and redundancy, and the ability to connect VPCs together. Overall, using subnets in AWS VPC can greatly enhance the flexibility and functionality of a cloud-based network.